English for Specific Purposes (ESP)
Definition of ESP :
There are almost as many definitions of ESP as the number of scholars who have attempted to define it. Many others have tried to define ESP in terms of what it is not rather than in terms of what it really is, but we will disregard their definitions to concentrate on finding out what ESP really means.
Mackay and Mountford (1978) defined ESP as the teaching of English for a “clearly utilitarian purpose” ( Mountford ,1978:2). The purpose they refer to is defined by the needs of the learners , which could be academic , occupational , or scientific . These needs in turn determine the content of the ESP curriculum to be taught and learned .
Mackay and Mountford also defined ESP and the special language that takes place in specific settings by certain participants . They stated that those participants are usually adults , they focused on adults because adults are usually highly conscious of he reasons to attain English proficiency in a determined field of specialization , and because adults make real use of special language in the special settings and adults and the role , usually auxiliary , that English plays in those particular settings for those particular people . Robinson (1980) defined ESP courses as ones in which participants have specific goals and purposes ( again , academic , occupational and scientific). On this ,she cited Strevens (1977) to emphasize that the purposes language learners have for using language are of paramount importance .
Most definitions of what ESP is concur on three key topics : the nature of language to be taught and used , the learners , and the settings in which the other two would occur. These three aspects of ESP are closely connected to each other , and can be combined to establish that ESP is the teaching of specific and unique English (specialized discourse) to learners ( adults in their majority ) , who will use it in a particular setting (laboratory, hospital, etc.) in order to achieve a utilitarian goal or purpose ( communicate linguistically correct) , which in turn will fulfill additional personal goals ( promotional , economical, etc.) what ESP specialists do not seem to agree on is what type of language should be taught ( vocabulary , register , jargon ,etc.) and how to teach it .
Historical Development of ESP
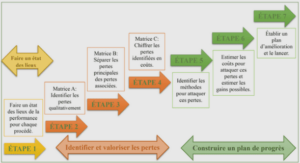
Hutchinson and Waters (1987) identified three key reasons they believe are common to the emergence of all ESP : the demands of a Brave New World, a revolution in linguistics and a focus on the learner . As to the first reason , they explain that two historical periods played an important role that led to the creation of ESP ; the end of the Second World War and the Oil Crisis in the 1970s . On the one hand , the end of the Second World War was an era of expansion in scientific , technical and economic activity world-wide . The role of international language fell obviously to English because of the economic expansion of the United States in the post –war world. On the other hand , the Oil Crisis of the early 1970s resulted in western money and knowledge flowing into the oil-rich countries . The language of this knowledge became English , this led consequently to exerting pressure on the language teaching profession , which boosted in this part of the world , to deliver the required goods . English now became subject to the wishes , needs and demands of people other than language teachers .
The second very important reason that had a tremendous impact on the emergence of ESP was revolution in linguistics . Most of the work of linguists in the 1960s and 1970s of the past century focused on the ways in which language is used in real communication contrary to the works of traditional linguists who set out to describe the features of language .
Hutchinson and Waters (1987) point out that one significant discovery was in the ways that spoken and written English vary . in other words , a particular context in which English is used would impose , in a way or another, the variant of English. This idea was taken one step further , if language in different situations varies , then tailoring language instruction to meet the needs of learners in specific contexts is also possible . Hence , in the 1960s and the early 1970s there were many attempts to describe English for Science and Technology .
The final reason that Hutchinson and Waters ( 1987) mention to have influenced the emergence of ESP has more to do with psychology than linguistics . More attention was given in the 1970s to the means through which a learner acquires a language and ways in which it is learnt . Hence,there was a shift of focus from methods of language learning to the different learning strategies , different skill , different learning schemata and different motivating needs and interests that are employed by different learners . This consequently led to a focus on learners’ need and designing specific courses to better meet individual needs .
Characteristics of ESP
Tony Dudley –Evans and Maggie Jo St John ( 1998) divided characteristic features of ESP in two groups according to its ‘ absolute’ and ‘ variable’ attributes . Concerning the absolute characteristics ( according to Dudley-Evans and St John ) :
• ESP is defined to meet specific needs of the learner .
• ESP makes use of the underlying methodology and activities of the discipline it serves.
• ESP is centered on the language ( grammar, lexis , register ) , skills, discourse and
genre appropriate to these activities .
The variable characteristics are seen in five points :
• ESP may be related to or designed for specific disciplines .
• ESP may use , in specific teaching situations , a different methodology from that of general English .
• ESP is likely to be designed for adult learners , either at a tertiary level institution or in a professional work situation .
• ESP is generally designed for intermediate or advanced students .
• Most ESP courses assume some basic knowledge of the language system ,but it can be used with beginners ( Dudley-Evans , 1998) .
Hutchinson and Waters ( 1992) do not emphasize any concrete limits of students’ level or age , they emphasize learners’ individual needs and specialist knowledge of using English for specific purposes . Although there exist several aims and different purposes why learning English , the way of learning may be same .
“ Though the content of learning may vary there is no reason to suppose that the processes of learning should be any different for the ESP learner than for the General English learner .” ( Hutchinson and Waters , 1992: 18). They add that ESP methodology “ could just have been used in the learning of any kind of English.” ( Hutchinson and Waters , 1992: 18 ).
General Introduction |