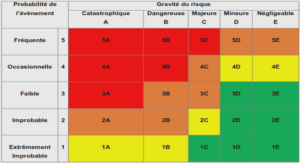
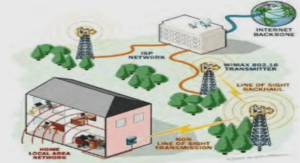
B.TECH. ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
9 Introduction, Interaction of Radiation with Matter –Quantum mechanical view. Essentials of Laser. Types of Laser He-Ne Laser, Ruby Laser, semiconductor Laser. Application of Lasers. Optical Fibers –Modes of Propagation, Types of optical fibers. Optical fiber communication system. Attenuation. UNIT-III SUPERCONDUCTIVITY 9 Discovery of superconductivity, , Heat Capacity, Isotope effect, persistent currents, effect of external magnetic field, critical; current density, Behavior of a perfect conductor, Meissner effect, London penetration depth. BCS Theory. Type of superconductors. Josephson effect (AC and DC). Applications – Maglevs, SQUIDS. UNIT -IV MAGNETIC AND DIELECTRIC MATERIALS 9 Introduction- Measurement of Magnetic Susceptibility-Magnetic materials (Dia, Para, Ferro, Antiferro and Ferri)- Magnetic moment of atom-Hard and soft magnetic materials- Hysteresis
curve – Applications-Dielectrics-– Electronic, ionic and orientational, space polarizations – Internal fields in solids – Polarization-Induced dipoles-Nonpolar and Polar dielectries- Clausius Mosotti equation-Dielectric loss. UNIT -V NANOTECHNOLOGY AND ADVANCED MATERIALS 9 Introduction– Nano phase materials – Synthesis – Plasma arcing – chemical vapour deposition – Sol gel method – Electro deposition – Ball milling – properties and application – Carbon nano tubes – types, fabrication methods – Arc method – Pulsed laser deposition – Structure, Properties and Application.
COURSE CONTENTS UNIT-I FUELS (9) Classification, Characteristics of fuel, Comparison between Solid, liquid and gaseous fuels, Combustion and chemical principles involved in it, Calorific value: gross and net calorific values. Solid Fuels: Coal: Classification, Analysis: Proximate and Ultimate analysis of coal and their importance, Metallurgical coke: Properties, Manufacture by Otto Hoffman process. Liquid Fuels: Petroleum: its chemical composition and fractional distillation, Synthetic Petrol: Fischer-Tropsch process and Bergius Process, Knocking and chemical structure, octane number and cetane number and their significance, Gaseous Fuels: Natural gas, artificial gas (water gas, producer gas, coal gas). Flue gas analysis – Orsat apparatus UNIT-II PHASE RULE AND ALLOYS (9) Statement and explanation of the terms involved- one component water system- condensed phase rule-construction of phase diagram by thermal analysis-simple eutectic systems (Lead- Silver system only) – Alloys – importance – ferrous alloys – Nichrome – stainless steel – non- ferrous alloys – brass and bronze. UNIT-III POLYMERS
(9) Polymer, Classification based on, origin, structure, chemical structure, Degree of polymerization Types of polymerization – Thermosetting and Thermoplastic polymers and their applications- Degradation of polymers, Conducting polymer and Biopolymers, Introduction to polymeric composites, Types of composite materials. UNIT-IV CORROSION AND ITS CONTROL (9) Chemical corrosion – Pilling – Bedworth rule – electrochemical corrosion – different types – galvanic corrosion – differential aeration corrosion – factors influencing corrosion – corrosion control – sacrificial anode and impressed cathodic current methods – corrosion inhibitors – protective coatings – paints – constituents and functions – metallic coatings – electroplating (Au) and electroless (Ni) plating. UNIT-V ENGINEERING MATERIALS (9) Refractories – Classification and properties, Lubricants- Classification and properties, Organic electronic materials – Solid oxide materials- Nano materials, Buckminister fullerenes.
9 Digital Computer Fundamentals–Block diagram of a computer–Components of a computer system–Applications of Computers–Hardware and Software definitions–Categories of Software–Booting–Installing and uninstalling Software–Software piracy–Software terminologies-Information Technology Basics–History of Internet–Internet Tools. UNIT II PROBLEM SOLVING METHODOLOGY 9 Problem solving Techniques–Program–Program development cycle–Algorithm – Flow chart – Pseudo Code – Program control structures – Types and generation of programming languages – Development of algorithms for simple problems. UNIT III INTRODUCTION TO C 9 Overview of C – Constants, Variables and Data Types – Operators and Expressions – Managing Input and Output operations – Decision Making – Branching and Looping. UNIT-IV FUNCTIONS