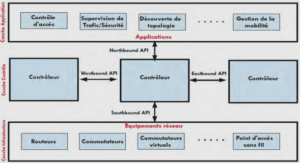
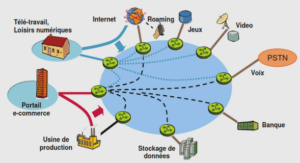
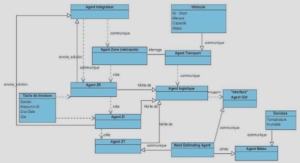
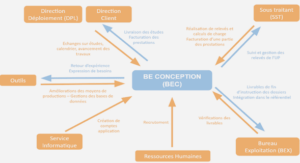
5.1 Why Scripting?
5.2 Benefits of using WMLScript
6 . WMLScript Core
6.1 Lexical Structure
6.1.1 Case Sensitivity
6.1.2 . Whitespace and Line Breaks
6.1.3 . Usage of Semicolons
6.1.4 Comments
6.1.5 Literals
6.1.5.1 .Integer Literals
6.1.5.2 Floating-Point Literals
6.1.5.3 String Literals
6.1.5.4 Boolean Literals
6.1.5.5 . Invalid Literal
6.1.6 Identifiers
6.1.7 Reserved Words
6.1.8 .Name Spaces
6.2 Variables and Data Types 8
6.2.1 . Variable Declaration
6.2.2 Variable Scope and Lifetime
6.2.3 Variable Access
6.2.4 . Variable Type
6.2.5 . L-Values
6.2.6 . Type Equivalency
6.2.7 Numeric Values
6.2.7.1 . Integer Size
6.2.7.2 .Floating-point Size
6.2.8 String Values
6.2.9 Boolean Values
6.3 Operators and Expressions 1
6.3.1 Assignment Operators
6.3.2 Arithmetic Operators
6.3.3 . Logical Operators
6.3.4 . String Operators
6.3.5 . Comparison Operators
6.3.6 Array Operators
6.3.7 Comma Operator
DOCUMENT STATUS
This document is available online in the following formats:
• PDF format at http://www.wapforum.org/.
Copyright Notice
© Wireless Application Protocol Forum Ltd. 1999. Terms and conditions of use are available from
the Wireless Application Protocol Forum Ltd. web site
(http://www.wapforum.org/docs/copyright.htm).
Errata
Known problems associated with this document are published at http://www.wapforum.org/.
Comments
Comments regarding this document can be submitted to WAP Forum in the manner published at
http://www.wapforum.org/.
REFERENCES
Normative references
[ECMA262] Standard ECMA-262: « ECMAScript Language Specification », ECMA, June 1997
[IEEE754] ANSI/IEEE Std 754-1985: « IEEE Standard for Binary Floating-Point Arithmetic ».
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, New York (1985).
[ISO10646] « Information Technology – Universal Multiple-Octet Coded Character Set (UCS) –
Part 1: Architecture and Basic Multilingual Plane », ISO/IEC 10646-1:1993.
[RFC2279] « UTF-8, a transformation format of Unicode and ISO 10646 », F. Yergeau, January
1998. URL: ftp://ftp.isi.edu/in-notes/rfc2279.txt
[RFC2068] « Hypertext Transfer Protocol – HTTP/1.1 », R. Fielding, et al., January 1997. URL:
ftp://ftp.isi.edu/in-notes/rfc2068.txt
[RFC2119] « Key words for use in RFCs to Indicate Requirement Levels », S. Bradner, March
1997. URL: ftp://ftp.isi.edu/in-notes/rfc2119.txt
[RFC2396] « Uniform Resource Identifiers (URI): Generic Syntax », T. Berners-Lee, et al.,
August 1998. URL: http://info.internet.isi.edu/in-notes/rfc/files/rfc2396.txt
[UNICODE] « The Unicode Standard: Version 2.0 », The Unicode Consortium, Addison-Wesley
Developers Press, 1996. URL: http://www.unicode.org/
[WAP] « Wireless Application Protocol Architecture Specification », WAP Forum,
30-April-1998. URL: http://www.wapforum.org/
[WML] « Wireless Markup Language Specification », WAP Forum, 04-November-1999.
URL: http://www.wapforum.org/
[WMLSLibs] « WMLScript Standard Libraries Specification », WAP Forum, 04-November-1999.
URL: http://www.wapforum.org/
[WSP] « Wireless Session Protocol », WAP Forum, 05-November-1999. URL:
http://www.wapforum.org/
[XML] « Extensible Markup Language (XML), W3C Proposed Recommendation 10-
February-1998, REC-xml-19980210 », T. Bray, et al, February 10, 1998. URL:
http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-xml
Informative References
[HTML4] « HTML 4.0 Specification, W3C Recommendation 18-December-1997, REC-
HTML40-971218 », D. Raggett, et al., September 17, 1997. URL:
http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-html40
[JavaScript] « JavaScript: The Definitive Guide », David Flanagan, O’Reilly & Associates, Inc.1997
[WAE] « Wireless Application Environment Specification », WAP Forum,04-November-1999. URL: http://www.wapforum.org/
DEFINITIONS AND ABBREVIATIONS
Definitions
The following are terms and conventions used throughout this specification.
The key words « MUST », « MUST NOT », « REQUIRED », « SHALL », « SHALL NOT », « SHOULD », « SHOULD NOT », « RECOMMENDED », « MAY » and « OPTIONAL » in this document are to be interpreted as described in [RFC2119].Bytecode – content encoding where the content is typically a set of low-level opcodes (ie,instructions) and operands for a targeted hardware (or virtual) machine.Client – a device (or application) that initiates a request for connection with a server.
…
WMLScript Language Specification (666 KO) (Cours PDF)