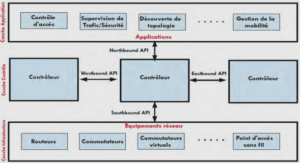
Cisco IOS Threat Defense Features
This chapter explores the advantages, concepts, and strategy behind the Cisco IOS Firewall offerings. Using a layered device as part of the overall security strategy allows the administrator great flexibility in access control. Using a demilitarized zone (DMZ) helps to isolate security breaches outside of the internal portion of the corporate network. If a security breach does occur, the rest of the network can remain intact. For example, “hacking” a web server that is positioned in a DMZ will not enable the hacker to penetrate into the internal portion of the network.In this chapter, you will examine the differences between packet filters, application layer gateways (ALG), and stateful packet filters, learn about the Cisco IOS Firewall feature set, and discover how the Cisco IOS Firewall operates. Chapter 22, “Implementing Cisco IOS Firewall Features,” covers how to implement the Cisco IOS Firewall.
“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz
The purpose of the “Do I Know This Already?” quiz is to help you decide whether you really need to read the entire chapter. If you already intend to read the entire chapter, you do not necessarily need to answer these questions now.CAUTION The goal of self-assessment is to gauge your mastery of the topics in this chapter. If you do not know the answer to a question or are only partially sure of the answer, you should mark this question wrong for purposes of self-assessment. Giving yourself credit for an answer that you correctly guess skews your self-assessment results and might provide you with a false sense of security.
Layered Device Structure
The Cisco IOS Firewall uses DMZs as a way of isolating services from the internal network. By creating a buffer zone, these DMZs create networks that are neither entirely internal nor entirely external to the corporate network. Traditionally, the DMZ exists between the corporate network and the Internet. There is no requirement for a DMZ to allow access from either the internal network or the Internet. For example, a payroll server could be attached to a DMZ that allows access only from the internal network. This would allow the administrator to restrict access to certain machines or users on the corporate network while ensuring that users on the Internet never even see the server.DMZ access is controlled by dedicated firewalls, such as the Cisco PIX Firewall, or by a router with multiple interfaces. Dedicated servers on the DMZ provide services such as web, FTP, or e-mail services. The DMZ may also host a gateway to applications that require outbound connectivity.
The primary advantage of a DMZ is that a security breach on one of the DMZ servers does not compromise the internal network. Using DMZs also encourages the administrator to compartmentalize the services onto dedicated servers, which may be extremely helpful in troubleshooting problems. When this compartmentalization is accomplished, it makes sense to place each server on its own DMZ.Configuring a network to use multiple DMZs is considered by many to be both state-of-the-art architecture and the best security practice available. Instead of placing all servers requiring access from the Internet into a single DMZ, placing each server into a separate DMZ has important advantages. Having each server on a dedicated DMZ not only makes it is easier for the administrator to change who is allowed access to an individual server but, more importantly, also is one of the best ways to ensure that the compromise of any single server does not affect any other portion of the network. Figure 21-2 shows a conceptual example of a network with multiple DMZs.
Packet filtering is the simplest technology used on the firewall. The difference between stateful and stateless is merely whether the filter tracks and responds to the context in which protocol requests are given. This technology limits traffic transiting the firewall by using an ACL. The ACL filters by IP address, port, or any other criterion within the assigned access list. Although packet filtering does allow great complexity and ease of use, it does not maintain a database of the current state of connections. Therefore, it is a less secure method than stateful packet filtering.An application layer gateway (ALG) uses a server that provides proxy services. The outside user connects to the ALG. The ALG then makes a connection to the interior server and passes requests between the interior server and the user. This is a very effective method for services such as HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, and e-mail. This method provides a good deal of security because the user connects to the DMZ server and never actually sees the interior server.